Comparing Artificial Sweeteners, Sugar Alcohols, and Natural Sweeteners: What’s the Difference?
Sweeteners play a crucial role in the supplement industry, enhancing flavour while keeping calorie content low. This article explores commonly used sweeteners like aspartame, sucralose, sugar alcohols, and natural alternatives such as stevia. We’ll discuss their properties, benefits, and potential risks, helping you make informed choices when selecting supplements or protein snacks.
CHECK OUT OUR OTHER BLOG ARTICLE: DEBUNKING SUPPLEMENT MYTHS: THE TRUTH ABOUT SUCRALOSE
Aspartame and Sucralose in Supplements
Aspartame, an artificial sweetener, is rarely used in supplements or protein snacks due to its sensitivity to heat and pH, which can degrade its level of sweetness. On the other hand, sucralose is commonly used in the supplement industry because it is heat-stable, water-soluble, and significantly sweeter than sugar, allowing manufacturers to use smaller quantities while maintaining desired sweetness levels.
Differentiating Sweeteners
Artificial sweeteners such as sucralose are often used in sugar-free products due to their intense sweetness and stability under various processing conditions. In contrast, natural sweeteners like stevia are derived from plants and provide sweetness without adding calories. Sucralose is about 600 times sweeter than sugar, while stevia’s key compounds, steviol glycosides, are 250-300 times sweeter.
What Are Sugar Alcohols and Natural Sweeteners?
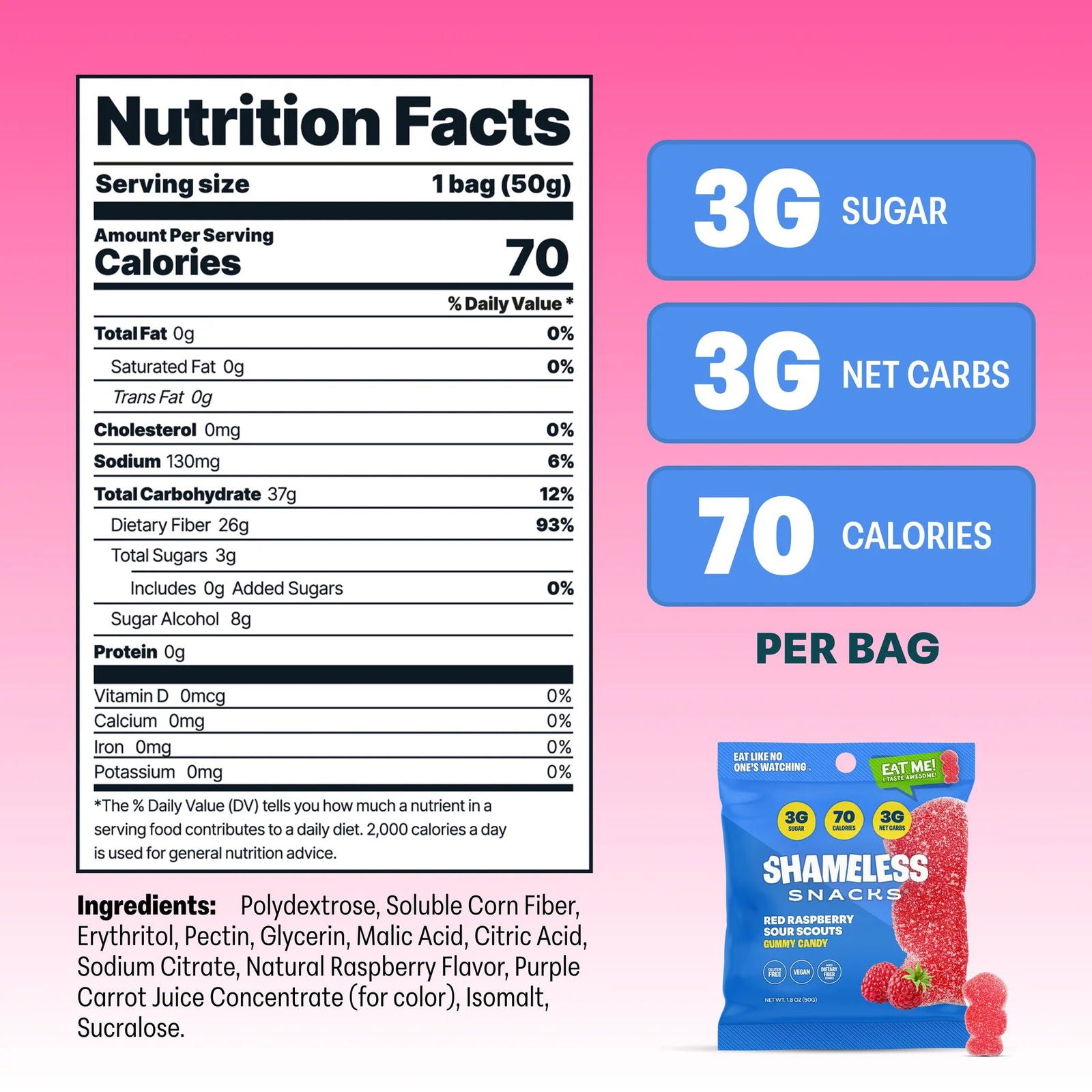
Sugar alcohols are low-digestible carbohydrates obtained through sugar hydrogenation. Common types include sorbitol, xylitol, and erythritol. They are popular in food products because they provide sweetness while contributing fewer calories and causing a lower glycemic response (Grembecka, 2015). Natural sweeteners like stevia come from Stevia rebaudiana, a plant known for its intensely sweet compounds (Peteliuka et al., 2021).
Differences from Sugar
Both sugar alcohols and stevia offer distinct advantages over traditional sugar. Sugar alcohols provide fewer calories, depending on the type (Grembecka, 2015). Stevia contains virtually no calories, making it an excellent option for weight management and blood sugar control (Peteliuka et al., 2021).
Sugar alcohols are absorbed slowly in the digestive system, minimizing spikes in blood sugar levels (Grembecka, 2015). Similarly, stevia has no glycemic impact, making it a suitable sugar substitute for diabetics (Peteliuka et al., 2021). Regarding sweetness, sugar alcohols are less sweet than sugar, while stevia is significantly sweeter, requiring only small amounts to match sugar’s sweetness.
Benefits
Sugar alcohols promote dental health by reducing cavity formation since oral bacteria cannot easily ferment them (Grembecka, 2015). They are suitable for diabetics due to their minimal effect on blood glucose levels. Additionally, they provide a cooling sensation in the mouth, enhancing products like chewing gum and mints.
Stevia offers several health benefits, including antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Studies indicate that it may help regulate blood pressure, support weight management, and improve metabolic health due to its non-caloric nature and bioactive compounds (Peteliuka et al., 2021).
Risks
Despite their benefits, both sugar alcohols and stevia have potential drawbacks. Excessive consumption of sugar alcohols can cause digestive issues such as bloating, gas, and laxative effects due to incomplete absorption in the gut (Grembecka, 2015). As previously mentioned, these are used in small quantities in protein snacks and treats and thus would likely not be consumed in excessive amounts.
Stevia is generally well tolerated but may cause mild digestive upset in sensitive individuals. Although regulatory agencies consider it safe, more research is needed to understand its long-term health impacts fully (Peteliuka et al., 2021).
References:
Grembecka, M. (2015). Sugar alcohols—their role in the modern world of sweeteners: A review. European Food Research and Technology, 241(1), 1-14. DOI: 10.1007/s00217-015-2437-7
Peteliuk, V., Rybchuk, L., Bayliak, M., Storey, K. B., & Lushchak, O. (2021). Natural sweetener Stevia rebaudiana: Functionalities, health benefits, and potential risks. EXCLI Journal, 20, 1412-1430. DOI: 10.17179/excli2021-4211